While Commercial UAV News largely focuses on real-world use cases that show how drones help businesses and organizations achieve their goals, it’s important to remember that there are many researchers working “behind the scenes” to move the technology forward and make UAV innovations a reality.
Recently, Commercial UAV News had the chance to speak with one of those researchers: Krishna Muvva, a PhD Candidate at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln, studying aerial robotics.
“My work involves artificial intelligence such as robotics, computer vision, and machine learning,” he explained. “And I’ve been studying ways to integrate MPC and neural network-based approaches to help drones achieve precise navigation, obstacle avoidance, and more robust control in complex environments.”
Through his work, Muvva looks to combine traditional and AI-based control methods and find ways to use advanced perception mechanisms to “allow UAVs to navigate and operate autonomously in dynamic settings such as public safety, critical infrastructure, and agriculture.”
For example:
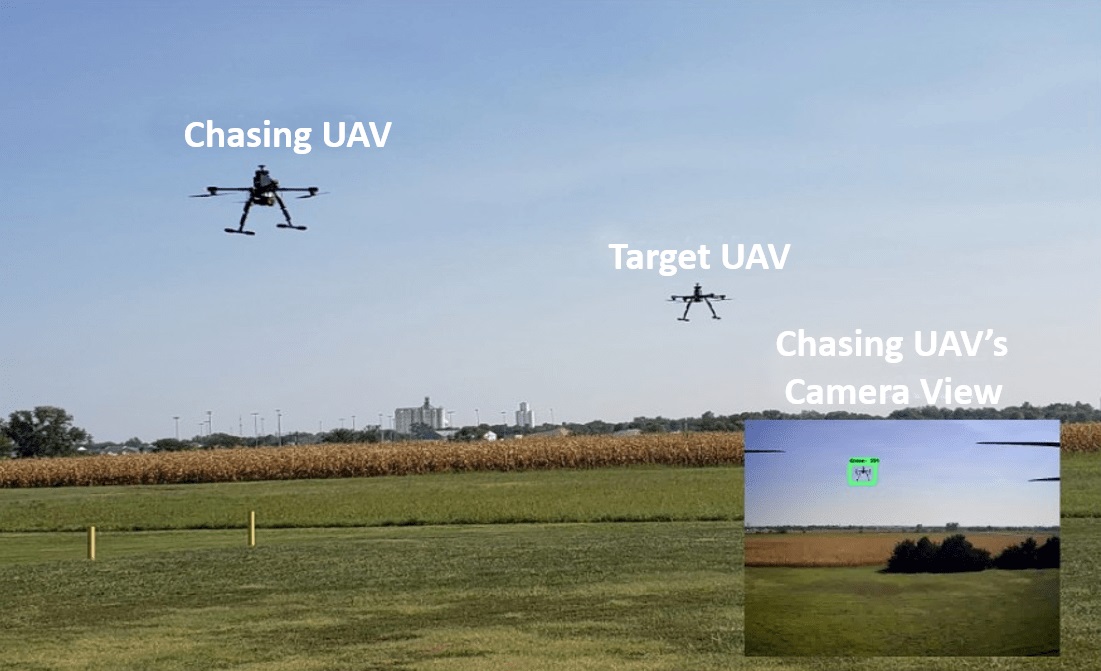
- A paper Muvva co-authored called “Cooperative Localization of UAVs in Multi-Robot Systems Using Deep Learning-Based Detection,” addresses the problem of how UAVs can achieve precise localization, especially when flying in close proximity. The paper describes how Muvva and his colleagues came up with a novel framework that “leverages deep learning-based detection” to enhance localization accuracy in multi-robot systems made up of UAVs and Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs). Through this approach, the researchers were able to improve “localization accuracy, even in challenging environments”—an advance that could enable better drone operations in fields such as agriculture, law enforcement, and mapping.
The video below showcases cooperative localization, where multiple UAVs collaborate to enhance positional awareness using deep learning-based detection and communication.
- Seeking to further integrate advanced technologies into drone operations, Muvva and his colleagues have looked to improve Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) perception for autonomous systems like drones. As described in their study, “Reliable AI for UAVs Through Control/Perception Co-Design,” the investigators looked at the challenges posed by the trade-off between latency and accuracy of CNNs. They developed a “situation-aware Model Predictive Control (MPC) to integrate perception and control modules.” Through both real-world and simulator tests, this approach was shown to help drones achieve optimal system performance.
For Muvva, these studies could pave the way for increased integration of AI in drone missions, leading to more efficient, accurate, and effective operations.
“As UAV applications expand into complex environments, achieving precise navigation, obstacle avoidance, and robust control becomes more critical,” he stated. “The application of hybrid MPC with neural networks for UAV adaptability in challenging environments shows the potential transformative potential of AI in UAV operations.”














Comments