Wonder Robotics, an Israeli-based start-up founded by a group of UAS and drone experts, focused on unlocking the business potential of drone urban services. Their aim is to reduce the need for personnel to operate drones, improve the safety and reliability of these services, and decrease dependence on well-trained drone pilots, communication infrastructure, and GPS.
Wonder Robotics’ Autonomy layer includes vertical awareness and robust precision landing, permitting drone safety beyond the operator/mission manager’s visual line of sight. In urban environments, this can prevent collisions with people and natural and infrastructural impediments such as trees, cables, buildings, and other dynamic environmental factors. Today, based on the regulation limitation and the reliability of the communication and GPS signal, most of the drone services need a visual observer or a safety officer to ensure a safe delivery or a safe landing back in the drone hub This means it's not sustainable in scale operations when it comes to generating revenue.
Furthermore, for every preplanned route the drone is taking, the service provider needs to plan for an emergency landing zone that is vacant from people or infrastructures in case the drone is in a situation where he needs to perform an urgent landing. This limits the drone service to semi-urban areas only, and, in most cases, it makes the drone mission longer than needed to fly near the emergency sites.
All of the above makes the cost of drone delivery simply more expensive than what the service provider afford to pay for the service.
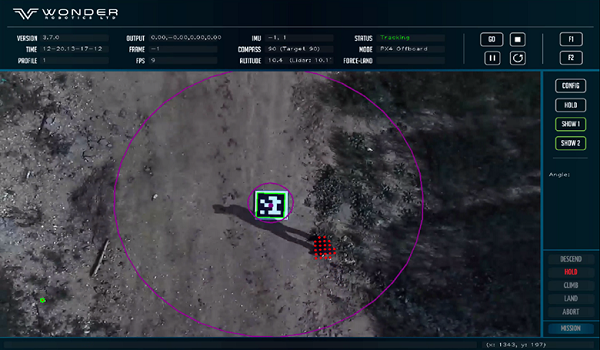
WonderLand 2.0, GPS denied for landing, safe hovering and close-range navigation
Wonder Robotics' first product, WonderLand, is very much like the Tesla Autopilot of commercial drones. Wonder Robotics technology is based on combining 2D semantic image processing and 3D point cloud processing, powered by additional AI algorithms. This system operates effectively at altitudes up to 100 meters. Using deterministic algorithms to take decisive actions in critical phases of the mission or for urgent landings in emergency landings.
In light of regulatory considerations, a non-deterministic algorithm, typically founded on AI and machine learning principles, initiates avoidance maneuvers based on the likelihood that an obstacle is a CAT with a 97% certainty. However, this approach is inadequate for compliance with future regulations.

WonderLand allows drones to detect power lines that need to be avoided, which helps to mitigate risks related to infrastructure damage, human injury, or damage caused to the drone directly from catching on these obstacles. This allows the drone to utilize robust precision landing and hovering that is not dependent on a visual observer, ground infrastructure, or mapping.
Wonderland has already been adopted by major drone organizations and sold commercially as a vertical awareness solution, contributing to more than 4,000 successful landings and operating daily around the world.
The upcoming version of Wonderland will incorporate features that enable drone and UAM (Urban Air Mobility) operations even without GPS. These capabilities encompass secure recovery in unforeseen and unmapped areas, as well as short-range navigation back to the point of origin. In contrast to costly military-grade GPS-denied navigation systems that hinge on pre-mapped base maps and pursue their objectives via alternate navigation paths, the WonderLand solution operates independently of data sources or alternative locations. This allows for an economical, secure hovering mode and the ability to fly to a safe landing site in the event of GPS signal loss.

Wonderland 2.0's GPS-denied capabilities will enable drone delivery companies to conduct operations below the city skyline. This can be achieved without requiring a visual observer or predetermined alternative landing locations in cases where GPS signals are disrupted due to multipath effects and reflections.
Ship to shore, shore-to-ship operation, WonderLand 2.0 maritime
An additional capability is addressing the growing market of maritime logistics and how drones are currently being used to deliver goods to ships to avoid having to bring smaller boats to the mainland for things like fresh food, medical supplies, or oil samples. Most drones need an operator to land on ships because of obstacles, unclear decks, or the limitations of placing additional infrastructure on deck to support autonomous drone landing. Currently, large ship or oil rigs operators have the option of using helicopters to bring in critical supplies or launching smaller boats to dock on shore. Neither of these options is ideal due to their high cost and low availability.
 WonderLand’s additional capability involves addressing the expanding maritime logistics market and the existing utilization of commercial drones for delivering goods and medical supplies to ships and oil rigs. Drones are an excellent alternative for dispatching smaller boats to the ship from the mainland for essentials like fresh food, medical supplies, or oil samples or helicopters. Drones are performing these tasks faster and safer, However, a common challenge emerges: most drone BVLOS operations require human operators to vertically navigate to the ship (it is always on the move), safe landing on ships due to obstacles like cables, unclear decks, or the limitation of installing additional infrastructure on the ship deck to enable autonomous drone delivery. WonderLand and its ability to vertically detect and avoid and robust precision landing without any marker allow maritime logistic drones services to be also highly cost-effective and safer.
WonderLand’s additional capability involves addressing the expanding maritime logistics market and the existing utilization of commercial drones for delivering goods and medical supplies to ships and oil rigs. Drones are an excellent alternative for dispatching smaller boats to the ship from the mainland for essentials like fresh food, medical supplies, or oil samples or helicopters. Drones are performing these tasks faster and safer, However, a common challenge emerges: most drone BVLOS operations require human operators to vertically navigate to the ship (it is always on the move), safe landing on ships due to obstacles like cables, unclear decks, or the limitation of installing additional infrastructure on the ship deck to enable autonomous drone delivery. WonderLand and its ability to vertically detect and avoid and robust precision landing without any marker allow maritime logistic drones services to be also highly cost-effective and safer.
About Wonder Robotics
Wonder Robotics aims to be the leading provider of intelligent and robust 360° self-awareness software for drones with layers that enable autonomous flight for commercial and military drones as well as eVTOLs powered by advanced vision-based technology. The company's product acts as a critical enabler in the rapidly evolving drone market, allowing for safe and autonomous operations that are a core aspect of emerging drone regulations and strongly advocated by industry leaders.
The technology is ideal for low-flying missions, including commercial package delivery, infrastructure inspection, mapping and advanced urban mobility for people (UAM). The company's vision is to expand its offering to include horizontal situational awareness for navigation, obstacle detection and avoidance, and safe precision landing, even in the absence of GPS.
















Comments