As businesses look for ways to obtain more insight into the health of their assets without impacting worker safety or operational efficiencies, imagery from drone surveys satisfy those requirements. Ardenna, an image processing and machine learning software developer for industrial inspections, recently launched Rail-Inspector, a new cloud-based software to accurately process and analyze imagery captured during drone surveys.
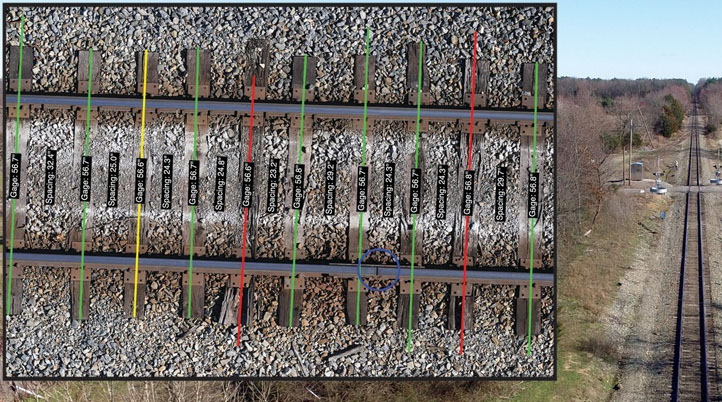
Developed after Bihrle Applied Research flew more than 100-mile BVLOS supplemental railway drone inspection flights for BNSF Railway, Ardenna’s new solution automates the detection, classification, and reporting of anomalies during rail inspections, to provide insightful, actionable data both more accurately and in a fraction of the time required by traditional inspection methods. Designed for Class 1 Railroads, Shortline Railroads, and Industrial Rail/Yards, Rail-Inspector analyzes tie condition/skew/spacing, track clearance, gage and rail gap measurement, joint bar detection, and more.
"Rail-Inspector takes images, whether 10 or 10,000, and generates a comprehensive dataset, representing details associated with the track's current health that would be impractical to obtain using other methods,” said David M. Patterson, Business Development Director for Ardenna. “By watching these track details evolve, trends can be identified, enabling maintenance to be scheduled and performed proactively before human or rail safety is impacted."
Using computer vision and machine learning algorithms, Rail-Inspector reduces maintenance downtime, increases operational efficiency, and improves worker and railroad safety. Additionally, it complies with the Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) Track Safety Standards (TSS) by generating data related to Track Geometry and Track Structure.
Within the Rail-Inspector Web Portal, users can upload, process, visualize, review, and download the collected data. It features a map view, to quickly get a visual indication of areas of concern, and more detailed views and tools to get right down to the pixel level and better understand the data. The portal also provides relational databases that can be easily integrated with custom business processes or 3rd party tools, such as ArcGIS, Tableau, Power BI, and Microsoft Excel.
To deliver the imagery and metadata in the form and specifications necessary for processing, Ardenna’s AI-based algorithms require a minimum of 12+ MP resolution images, 3.0 mm Ground Sample Distance (GSD), 10-15% image overlap, an automated flight profile, a NADIR camera angle, and RAW image format. “Rail owners interested in highly accurate gage measurements will require a LiDAR unit to capture accurate altitude,” says the company’s website. “Rail owners interested in joint bar assessment will require an offset image capture methodology in addition to the NADIR capture methodology.”
While many platforms are compatible with Ardenna’s technology, including manned aircraft, the company recommends three proven-platforms that meet the requirements to extract meaningful data from aerial imagery: Latitude HQ-60, Ardenna M600 (uses DJI M600 Pro airframe), and DJI Mavic 2 Zoom. In the future, Ardenna will launch a new configuration that will capture data from an operational rail vehicle.
Leveraging the success of Rail-Inspector, Ardenna will continue to develop new commercial solutions with its intelligent automation capabilities, and bring it to other industry sectors, including Energy and Telecommunications.














Comments